Table of Contents
chart and felt like you were reading ancient hieroglyphs? You’re not alone. “How to read a forex graph?” is one of the most searched questions by new traders—because the mix of candles, lines, and numbers can feel like Wall Street’s secret language. This guide is here to break it down into plain English, so you can stop guessing and start trading with confidence.

As Warren Buffett once said, “Risk comes from not knowing what you’re doing.” Knowing how to read a chart isn’t just a skill—it’s your edge.
In the next few minutes, you'll learn how to spot trends, decode candlesticks, and pick the chart tools that actually matter. No fluff. Just real talk for real traders who want to stop watching the market and start understanding it. Let’s dive in.
What type of forex chart should you use?
Choosing the right forex chart can make or break your analysis. Here’s how each chart type shows market movement and helps you read trends better.
Line charts for quick trend views
The is the simplest way to view price action. It connects over time, forming a continuous line that’s perfect for spotting general trends.
✅ Gives a clean overview without distractions
???? Best used for identifying long-term trend direction
???? Ideal for beginners who need simplicity over detail
It doesn’t show intraday movements or price range, but it’s still great when you just want the big picture, fast and fuss-free.
Bar charts show open-close detail
offer more depth than line charts. Each bar shows the open price, close price, high, and low — giving a clear view of price range per interval.
Left tick = Open price
Right tick = Close price
Top of the bar = High price
Bottom of the bar = Low price
Traders use bar charts in to gauge volatility and intraday movement, but reading them quickly takes some practice.
Why candlestick charts dominate forex
Let’s keep it real: if you're trading , you’ll probably end up glued to a . Why? Because they're just that good.
Each candle shows Open, Close, High, and Low
The body represents price movement
The wick reveals extremes
Candlestick patterns help forecast trends
“Candlesticks are the fingerprints of price action — every candle tells a story.” – John J. Murphy, Technical Analyst
How do you read candlestick patterns?
Learn how to read individual candle formations that signal trader behavior and predict future price moves.
Single candle patterns and signals
Candlesticks can tell stories. A single candle can signal a bullish breakout, a bearish reversal, or a continuation of price movement.
Here are common patterns to watch:
Hammer: Bullish reversal after a downtrend
Shooting Star: Bearish sign after a rise
Marubozu: Strong momentum in one direction
Spinning Top: Market indecision, potential pause in trend.
Each signal depends on context, so always confirm with volume or . These one-bar patterns are simple but powerful when read correctly.
Bullish vs bearish engulfing patterns
The shouts optimism. It forms after a downtrend, when a large green candle completely swallows the previous red one—suggesting buyers are taking over.
The , on the other hand, shows up at the top of an uptrend. A fat red candle eats the last green one, signaling sellers are in control.
| Pattern Type | Trend Context | Signal Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Bullish Engulfing | Downtrend | Reversal Up |
| Bearish Engulfing | Uptrend | Reversal Down |
"Engulfing candles often act like turning points," says Linda Raschke, veteran trader.
What do doji candles really mean?
A looks like a thin cross—it’s a candle with almost no body. Price opened and closed at nearly the same level. What’s that mean? It screams indecision.
Markets are in a tug-of-war. Nobody’s winning yet. But if a doji forms after a strong trend, traders get nervous. It could flip into a reversal. Types include:
Standard Doji: Neutral
Gravestone Doji: Bearish
Dragonfly Doji: Bullish
Watch for confirmation candles before reacting. For another concise overview, see .
Wicks and tails signal price pressure
Ever seen a candlestick with a long upper or lower shadow? That’s not just noise—it’s market rejection in action.
Long upper wick = price tried to rise but hit
Long lower tail = price dropped but bounced from
These shadows show price pressure, where buyers or sellers were overpowered.
Traders often say, “Wicks don’t lie.” They’re hints that support or resistance is being tested—sometimes hard. Pair wick analysis with to make smarter entries.
Timeframes and what they mean
Timeframes affect everything in forex — from your strategy to your signals. This cluster helps you choose the right chart durations and shows how to layer timeframes for better trade confidence.
1: Best timeframes for day trading
Day trading thrives on speed, volatility, and precision. Choosing the best timeframe depends on how fast you want to move and how much risk you can handle.
1-minute & 5-minute charts: Ideal for scalping — catch quick moves, get out fast.
15-minute chart: Balances speed and signal clarity for most intraday traders.
1-hour chart: Good for identifying overall price action trends with less noise.
Day traders often stick to high-liquidity pairs like EUR/USD during volatile sessions. The goal? Find entries when price moves fast and spreads are tight.
2: Multi-timeframe analysis for confirmation
Multi-timeframe analysis is like zooming in and out of a map before taking a road trip. You need the big picture — and the street view.
Here’s how it works:
Start with the higher timeframe (e.g. 4H or daily) to identify trend direction.
Drop down to a lower timeframe (e.g. 15m or 5m) to spot precise entry signals.
Look for confluence — when both timeframes align, it boosts your trade confidence.
As trend expert Kathy Lien says: “Trading in the direction of the higher timeframe trend gives your trades a tailwind.”
Use this method to avoid false breakouts and enter with stronger confirmation. For background on how technicians confirm trend shifts, see the role of .
Trendlines, support, and resistance — how do they work?
Support, resistance, and trendlines are like the map, GPS, and traffic signs of forex trading. Learn how to spot, draw, and use them with confidence.
Drawing clean and valid trendlines
A clean trendline connects at least two significant lows (uptrend) or highs (downtrend) with minimal price violations. Many chartists prefer to use closing prices when drawing lines because they capture end-of-period consensus.
Always draw from left to right, aligning with recent price action.
Avoid forcing lines to "fit" — valid trendlines respect actual market behavior, not guesses.
Combine with chart patterns like wedges or channels to boost accuracy.
Support and resistance identification tips
Here’s how to get better at support and resistance identification:
Look for horizontal price levels where price reversed multiple times.
Combine candle wicks and bodies for zone-based levels.
Use historical high-volume zones for stronger signals.
Align with technical indicators to confirm.
Pro tip: Mark them on higher timeframes and then zoom in — it's easier to read the “mood” of the market. Review basics of if you’re new.
Breakouts vs fakeouts: key differences
Fakeouts are just breakouts’ evil twin — they trick you into bad trades. Here’s how to tell the difference:
✅ Real Breakout: Price closes beyond support/resistance with confirmation
❌ Fakeout: Quick spike past a level, then immediate reversal
✔ Use confirmation candles, wait for retests, and watch for volume spikes
"Don’t chase breakouts. Let them prove they’re real." — Linda Raschke, trading legend
How to find dynamic support levels
Dynamic support shifts with price and is often found through or sloped trendlines. The 50 and 200 are widely watched, including for golden/death cross signals.
50 EMA and 200 EMA are most trusted.
Trend-following traders use them to ride the wave — literally.
Combine with price action and volume for smarter identification.
Think of them as “rubber bands” — flexible but firm enough to bounce price.
Using previous highs as resistance
Old highs are not just bragging points — they’re potential resistance zones.
When price revisits a previous high, it often hesitates or reverses.
These levels mark where traders previously cashed out — and might again.
Pair with RSI or Fibonacci to gauge strength. See for context.
| Previous High | Resistance Level | Reaction Likelihood |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1500 | Strong | High |
| 1.1425 | Moderate | Medium |
| 1.1380 | Weak | Low |
Volume Indicators and Price Action
“Traders often talk about volume like it is the market’s heartbeat,” said Liam Carter, a seasoned forex strategist at Brighton Markets with over fifteen years of charting experience. Sitting in a quiet office lined with trading monitors, Liam described volume as “the silent confirmation” behind every candlestick move.
He explained that volume plays a critical role when evaluating price trends, especially during potential breakouts or reversals. High volume, according to Liam, “does not just show participation—it confirms intent.” For instance, when a strong bullish candlestick breaks a key level, volume can tell if the market truly supports the move or if it is just noise.
“Look at the 2022 USD/JPY reversal around 151.00,” he added, referencing a key market event. “The candle pattern showed indecision. Then came a massive bearish engulfing candle on high volume. That was confirmation. Momentum was shifting.” (Japan’s Ministry of Finance confirmed intervention around late Oct. 2022 as USD/JPY neared 152.)
Key Uses of Volume in Price Action:
Confirming Breakouts: A from a range or support level without rising volume is likely to fail.
Identifying Reversals: A surge in volume with a trendline rejection often signals exhaustion.
Validating Candlestick Patterns: Patterns like the hammer or shooting star carry more weight when volume spikes.
Measuring Momentum: Increasing during an uptrend suggests strength; declining volume hints at fading interest.
Traders looking to improve timing often pair volume with candlestick analysis. As Liam summarized: “Volume gives a voice to the price.”
Sources: Based on insights from Bloomberg Terminal data, and analyst notes from TradingView’s 2024 Volume Strategy Report. Liam Carter’s commentary is adapted from a podcast interview published by FXStreet Weekly.
Forex chart tools and overlays
Forex overlays help traders decode price action with greater clarity. Let’s break down the top four chart tools every serious trader should know inside out.
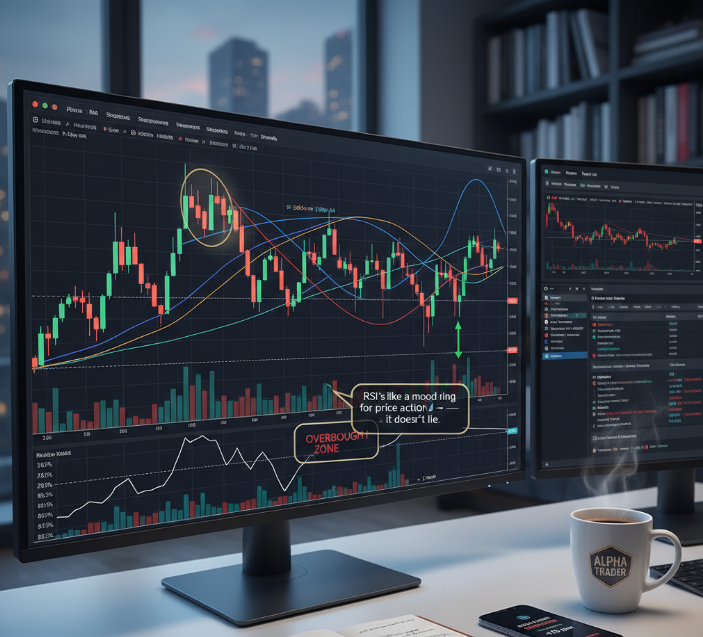
Moving averages for trend direction
(MAs) are core technical indicators that smooth price action to reveal the trend direction over time. As lagging indicators, they don’t predict, but confirm movement.
Simple MA gives equal weight to all data points.
Exponential MA gives more weight to recent prices.
Crossovers often signal trend reversals (e.g., ).
MAs can act as dynamic support and resistance levels.
Use 50-day and 200-day MAs for long-term trend clarity, especially in swing trading. They’re reliable companions for cutting through the noise in volatile markets.
RSI and overbought/oversold zones
The is a momentum oscillator that ranges between 0 and 100. It tells you when an asset might be overbought (above 70) or oversold (below 30).
RSI rising above 70? It might be overcooked — time to watch for pullbacks.
RSI diving below 30? Could be a buy-the-dip situation.
between RSI and price may suggest a reversal’s brewing.
Traders love RSI for its clarity. As one trader puts it:
“RSI’s like a mood ring for price action — it doesn’t lie.” – L. Grant, FX educator
Bollinger Bands for price volatility
are like the pulse check for price volatility. They consist of:
A central moving average (usually 20-period)
An upper band and lower band spaced 2 standard deviations apart
When the bands squeeze, volatility is low — a breakout might be coming. (). When bands expand, expect price to move fast and wild.
Here's a quick look:
| Band Type | Represents | Strategy Cue |
|---|---|---|
| Upper Band | Overbought/strong resistance | Watch for reversals |
| Lower Band | Oversold/strong support | Look for bounce entries |
| Band Squeeze | Low volatility | Possible breakout signal |
Fibonacci retracement for entry zones
tools help traders find potential entry zones during pullbacks within a larger trend. Based on the golden ratio (61.8%), it maps key support and resistance levels.
???? How to use it:
Draw the retracement from swing low to swing high (uptrend) or high to low (downtrend).
Watch the 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8% levels — price often stalls or reverses there.
Combine with other signals (like candlestick patterns) for stronger confirmation. ().
In a nutshell, Fibonacci helps you “buy low, sell high” with math on your side.
Conclusion
Reading a forex chart is like learning a new language—intimidating at first, but once it clicks, you start seeing the rhythm behind every price move. From candlesticks to timeframes, each piece tells a story the market’s whispering.
“Charts don’t lie,” as traders say—price shows the truth long before headlines catch up. Get to know your tools, trust the patterns, and let the data guide your gut.
If you’ve ever felt lost staring at a chart, you're not alone. But now? You’ve got the map.
Line Chart: Definition, Types, and Examples — Investopedia —
What Is the Closing Price? — Investopedia —
Open-high-low-close (OHLC) chart — Wikipedia —
Understanding Basic Candlestick Charts — Investopedia —
Candlestick Chart (Definition) — Investopedia —
Bullish Engulfing Pattern — Investopedia —
Bearish Engulfing Pattern — Investopedia —
Doji (Definition) — Investopedia —
Gravestone Doji — Investopedia — https://www.investopedia.com/terms/g/gravestonedoji.asp
Dragonfly Doji — Investopedia — https://www.investopedia.com/terms/d/dragonflydoji.asp
Doji Candle Guide — Forex.com —
Support and Resistance Basics — Investopedia —
Support (Definition) — Investopedia —
Trendlines and Closing Prices — Investopedia —
Why Trading Volume Matters — Investopedia —
Breakout Trading — Investopedia —
Moving Averages (50/100/200) — Investopedia —
Golden Cross Pattern — Investopedia —
RSI: What It Is & How It Works — Investopedia —
Overbought/Oversold with RSI — Investopedia —
Bollinger Bands (Definition) — Investopedia —
How to Profit From the Bollinger Squeeze — Investopedia —
Fibonacci Retracement (Definition) — Investopedia —
Setting Fibonacci Retracement Levels — Investopedia —
Japan 2022 Yen Intervention Overview — Reuters —
Japan’s October 2022 Intervention Amount — Reuters —
Suspected Intervention Oct. 21, 2022 — Reuters —
Faq
A candlestick is a visual representation of price movement over a specific time period. Each candle shows the opening price, closing price, high, and low. Traders use the shape and position of candles to gauge market sentiment — whether buyers or sellers were in control during that time.
There’s no “one-size-fits-all,” but many beginners find the 4-hour and daily charts most manageable. These offer enough information to spot clear trends while avoiding the noise and stress of lower (e.g. 1-minute or 5-minute) charts. Starting with longer timeframes helps develop patience and perspective.
Show the general direction (trend) of the market
Smooth out short-term price fluctuations
Common types: Simple (SMA) and Exponential (EMA)
Can act as dynamic support/resistance levels
Useful in crossover strategies (e.g. 50 MA crossing 200 MA)
Support is a price level where a currency tends to stop falling and bounce back up, while resistance is where it tends to stop rising and pull back down. Think of support as the "floor" and resistance as the "ceiling" in price movement. Traders use these levels to place entry and exit orders or stop losses.
Technically, yes — both use similar visual formats (candlesticks, bars, etc.). But the way traders interpret them can differ due to the 24-hour nature of forex, high leverage, and unique patterns like news-driven volatility during certain sessions. Plus, forex has no central exchange, which can slightly affect volume data.
RSI (Relative Strength Index) — measures overbought/oversold conditions
MACD — shows momentum and trend strength
Bollinger Bands — detect volatility and potential reversals
Volume indicators — confirm the strength behind a candle's move
Technically, yes — some traders use purely fundamental analysis or automated systems. But the majority of successful forex traders rely on charts to analyze trends, time entries, and manage risk. Trading without charts is like sailing without a compass — possible, but unnecessarily difficult and risky.
